Practice: Submit HTC Jobs using HTCondor
Purpose
This guide discusses how to run jobs on the CHTC using HTCondor.
Workflow Overview
The process of running computational workflows on CHTC resources follows the following outline:
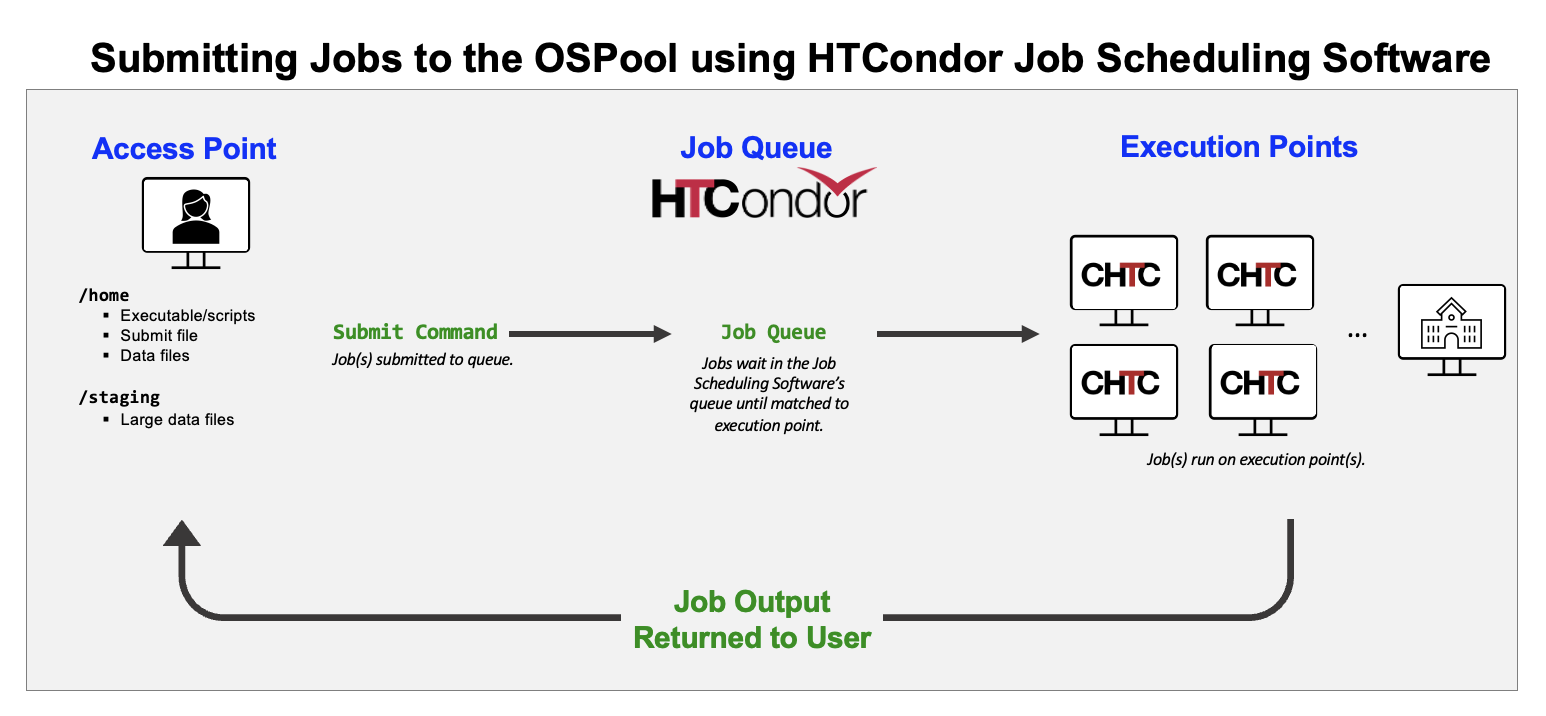
Terminology:
- Access point is where you login and stage your data, executables/scripts, and software to use in jobs.
- HTCondor is a job scheduling software that will run your jobs out on the execution points.
- The Execution Points is the set of resources your job runs on. It is composed of servers, as well as other technologies, that compose the cpus, memory, and disk space that will run the computations of your jobs.
Run Jobs using HTCondor
We are going to run the traditional ‘hello world’ program with a CHTC twist. In order to demonstrate the distributed resource nature of CHTC’s HTC System, we will produce a ‘Hello CHTC’ message 3 times, where each message is produced within is its own ‘job’. Since you will not run execution commands yourself (HTCondor will do it for you), you need to tell HTCondor how to run the jobs for you in the form of a submit file, which describes the set of jobs.
Note: You must be logged into a CHTC Access Point for the following example to work.
🎞️ Demo: Submit HTC Jobs using HTCondor
You can follow along with the job submission tutorial outlined in this guide in video format.
You may notice that the example in the video is slightly different—it uses
executableandargumentsin the submit file instead ofshell. This is reflects an older submit convention, however, either case still works!
Prepare job executable and submit file on an Access Point
-
First, create the executable script you would like HTCondor to run. For our example, copy the text below and paste it into a file called
hello-world.sh(we recommend using a command line text editor) in your home directory.#!/bin/bash # # hello-world.sh # My CHTC job # # print a 'hello' message to the job's terminal output: echo "Hello CHTC from Job $1 running on `whoami`@`hostname`" # # keep this job running for a few minutes so you'll see it in the queue: sleep 180Let’s test this script locally. First, let’s add executable permissions to the script with the
chmodcommand, which allows us to execute the code.chmod +x hello-world.shTest the code by typing the following line:
./hello-world.sh 0You should see a message printed to the terminal, like so:
[alice@ap2002 hello-world]$ ./hello-world.sh 0 Hello CHTC from Job 0 running on alice@ap2002The terminal will pause for 3 minutes, as specified by
sleep 180in our script. Cancel the pause time by pressingCTRL + C. Now we’ve successfully run the script locally!However, to run it on CHTC, we will use our HTCondor submit file to run the
hello-world.shexecutable and to automatically pass different arguments to our script.⚠️ Do not test your full workload directly on the Access Points!
Simple scripts, such as this example, which use few compute resources, are safe to test, but any script or executable that requires computing power or excessive memory should be tested inside of a job.
-
Prepare your HTCondor submit file, which you will use to tell HTCondor what job to run and how to run it. Copy the text below, and paste it into file called
hello-world.sub. This is the file you will submit to HTCondor to describe your jobs (known as the submit file).# hello-world.sub # Specify your executable (single binary or a script that runs several # commands) and arguments to be passed to jobs. # $(Process) will be a integer number for each job, starting with "0" # and increasing for the relevant number of jobs. shell = ./hello-world.sh $(Process) # Specify the name of the log, standard error, and standard output (or # "screen output") files. Wherever you see $(Cluster), HTCondor will insert the # queue number assigned to this set of jobs at the time of submission. log = hello-world_$(Cluster)_$(Process).log error = hello-world_$(Cluster)_$(Process).err output = hello-world_$(Cluster)_$(Process).out # Transfer our executable script transfer_input_files = hello-world.sh # Requirements (e.g., operating system) your job needs, what amount of # compute resources each job will need on the computer where it runs. request_cpus = 1 request_memory = 1GB request_disk = 5GB # Run 3 instances of our job: queue 3By using the “
$1” variable in our hello-world.sh executable, we are telling HTCondor to fetch the value of the argument in the first position in the submit file and to insert it in location of “$1” in our executable file.Therefore, when HTCondor runs this executable, it will pass the
$(Process)value for each job and hello-world.sh will insert that value for “$1” in hello-world.sh.More information on special variables like “
$1", “$2”, and “$@” can be found here. -
Now, submit your job to HTCondor’s queue using
condor_submit:[alice@ap2002]$ condor_submit hello-world.subThe
condor_submitcommand actually submits your jobs to HTCondor. If all goes well, you will see output from thecondor_submitcommand that appears as:Submitting job(s)... 3 job(s) submitted to cluster 36062145. -
To check on the status of your jobs in the queue, run the following command:
[alice@ap2002]$ condor_qThe output of
condor_qshould look like this:-- Schedd: ap2002.chtc.wisc.edu : <128.104.101.92:9618?... @ 04/14/23 15:35:17 OWNER BATCH_NAME SUBMITTED DONE RUN IDLE TOTAL JOB_IDS Alice ID: 3606214 4/14 12:31 2 1 _ 3 36062145.0-2 3 jobs; 2 completed, 0 removed, 0 idle, 1 running, 0 held, 0 suspendedYou can run the
condor_qcommand periodically to see the progress of your jobs. By default,condor_qshows jobs grouped into batches by batch name (if provided), or executable name. To show all of your jobs on individual lines, add the-nobatchoption. -
When your jobs complete after a few minutes, they’ll leave the queue. If you do a listing of your
/homedirectory with the commandls -l, you should see something like:[alice@submit]$ ls -l total 28 -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 0 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_0.err -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 60 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_0.out -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 0 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_0.log -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 0 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_1.err -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 60 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_1.out -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 0 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_1.log -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 0 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_2.err -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 60 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_2.out -rw-r--r-- 1 alice alice 0 Apr 14 15:37 hello-world_36062145_2.log -rw-rw-r-- 1 alice alice 241 Apr 14 15:33 hello-world.sh -rw-rw-r-- 1 alice alice 1387 Apr 14 15:33 hello-world.subUseful information is provided in the user log, standard error, and standard output files.
HTCondor creates a transaction log of everything that happens to your jobs. Looking at the log file is very useful for debugging problems that may arise. Additionally, at the completion of a job, the .log file will print a table describing the amount of compute resources requested in the submit file compared to the amount the job actually used. An excerpt from hello-world_36062145_0.log produced due the submission of the 3 jobs will looks like this:
… 005 (36062145.000.000) 2023-04-14 12:36:09 Job terminated. (1) Normal termination (return value 0) Usr 0 00:00:00, Sys 0 00:00:00 - Run Remote Usage Usr 0 00:00:00, Sys 0 00:00:00 - Run Local Usage Usr 0 00:00:00, Sys 0 00:00:00 - Total Remote Usage Usr 0 00:00:00, Sys 0 00:00:00 - Total Local Usage 72 - Run Bytes Sent By Job 265 - Run Bytes Received By Job 72 - Total Bytes Sent By Job 265 - Total Bytes Received By Job Partitionable Resources : Usage Request Allocated Cpus : 0 1 1 Disk (KB) : 118 1024 1810509281 Memory (MB) : 54 1024 1024 Job terminated of its own accord at 2023-04-14T17:36:09Z with exit-code 0.And, if you look at one of the output files, you should see something like this:
Hello CHTC from Job 0 running on alice@e389.chtc.wisc.edu.
Congratulations. You’ve run an HTCondor job!
Important Workflow Elements
Removing Jobs
To remove a specific job, use condor_rm <JobID, ClusterID, Username>.
Example:
[alice@ap2002]$ condor_rm 845638.0
Test and Optimize Resources
-
Examine Job Success. Within the log file, you can see information about the completion of each job, including a system error code (as seen in “return value 0”). You can use this code, as well as information in your “.err” file and other output files, to determine what issues your job(s) may have had, if any.
-
Improve Efficiency. Researchers with input and output files greater than 1GB, should store them in their
/stagingdirectory instead of/hometo improve file transfer efficiency. See our data transfer guides to learn more. -
Get the Right Resource Requests Be sure to always add or modify the following lines in your submit files, as appropriate, and after running a few tests.
Submit file entry Resources your jobs will run on request_cpus = cpus Matches each job to a computer "slot" with at least this many CPU cores. request_disk = kilobytes Matches each job to a slot with at least this much disk space, in units of KB. request_memory = megabytes Matches each job to a slot with at least this much memory (RAM), in units of MB. -
Determining Memory and Disk Requirements. The log file also indicates how much memory and disk each job used, so that you can first test a few jobs before submitting many more with more accurate request values. When you request too little, your jobs will be terminated by HTCondor and set to “hold” status to flag that job as requiring your attention. To learn more about why a job as gone on hold, use
condor_q -hold. When you request too much, your jobs may not match to as many available “slots” as they could otherwise, and your overall throughput will suffer.
Use shell or executable/arguments in your submit file
You can either use shell or executable and arguments in your submit file to specify how to run your jobs.
Option 1: Submit with shell
You can use shell to specify the whole command you want to run.
shell = ./hello-world.sh $(Process)
transfer_input_files = hello-world.sh
When using shell, consider:
- Do you need to transfer your executable? You may need to add your executable script (i.e.,
hello-world.sh) in thetransfer_input_filesline, as HTCondor does not have the ability to autodetect scripts to be transferred. - If you are using
./to execute your code, as in the example above, ensure your shell script has executable permissions with thechmod +x <script>command. - Alternatively, you may use a shell like
bashto execute your code, (i.e.,shell = bash hello-world.sh 0). When you use this option, you do not have to give your shell script executable permissions. - Keep your
shellscript simple; quoting and special characters may throw errors. If you need complex scripting, we recommend writing a wrapper script.
Option 2: executable and arguments
In this convention, you break your command into two parts—the executable and the arguments.
executable = hello-world.sh
arguments = $(Process)
When using this option:
- HTCondor will transfer your executable by default. You do not need to list your executable in
transfer_input_files. - You do not have to add a
./or/bin/bashto the beginning of yourexecutableline. - You do not have to give your
executablescript executable permissions.